Geography Class 02
The shape of the earth (5:10 PM)
- The earth is Flattened at the pole and bulged at the equator.
- It is due to the continuous rotation of the earth.
- This shape is called a geoid or oblate spheroid.
- Evidence of the geoid shape of the earth:
- Circumnavigation of the earth- Magellan completed the first circumnavigation in 1519.
- Circular horizon- The horizon appears circular when viewed from a high vantage point and the horizon widens with the increase in altitude.
- Ship's visibility- A ship appears to be rising from water when viewed from the coast or a ship(Bedford level experiment also proves the spherical shape).
- Sunrise and sunset- Different timing of sunrise and sunset at different locations.
- Eclipse- The earth's circular shadow falls on the moon during a lunar eclipse.
- Other planetary bodies- Since all other planetary bodies are spherical, the earth should also be spherical since the earth is also a part of the same solar system.
Latitude and longitude (5:46 PM)
- Latitude:
- Diagramatic representation of latitude:
-
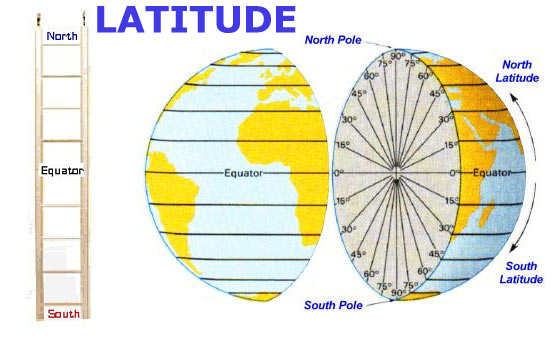
- The angular distance of the point on the earth’s surface measured in degrees from the centre of the earth towards north & south of the equator is called the Latitude.
- Parallels of latitudes are the imaginary lines connecting places with the same latitude.
- The largest parallel of latitude is zero degrees and is called the equator.
- The parallels of latitudes are always parallel to the equator and one another.
- The length of the latitude decreases from the equator towards the north pole and south pole, however, the distance between them remains the same.
- The distance between one degree of latitude is equal to 111 km anywhere on the earth.
- Longitude:
- Diagramatic representation of longitude:
-

- Longitude is the angular distance of a place east or west of the prime meridian.
- Meridians are the semi circles running from pole to pole connecting places with the same longitude.
- The meridians of longitudes are not parallel to each other.
- The distance between them is maximum at the equator and decreases towards the pole.
- The distance between two meridians separated by 1 degree is equal to 111 km at the equator and it gradually decreases and is zero at the pole.
- The length of the meridian always remains the same.
- Great circle:
- It is the longest possible circumference that can be drawn on earth.
- A great circle divides the earth into 2 equal halves.
- An infinite number of great circles can be drawn on the surface of the earth.
- A Great circle is used to find the shortest distance between two locations on the surface of the earth.
The rotation of the earth (7:02 PM)
- The spinning motion of the earth on its axis is called the rotation of the earth.
- The axis of rotation is the imaginary line passing through poles and the centre of the earth around which the earth rotates.
- The orbital plane is the plane in which the earth orbits around the sun.
- The angle between the axis of rotation and the orbital plane is 66.5 degrees.
- The angle of tilt of the axis of rotation from its normal position is equal to 23.5 degrees.
- The direction of rotation is counterclockwise or West to East.
- Period of rotation:
- Solar Day: The time taken by the earth to rotate on its axis so that the sun appears in the same position in the sky is called Solar day.
- The solar day is equal to 24 hours.
- Sidereal day: The time is taken for the earth to rotate on its axis so that a distant star appears in the same position in the sky is called a Sidereal day.
- The sidereal day is equal to 23 hrs 56min.
- Diagramatic representation of solar day Vs sidereal day:
-

- Speed of earth’s rotation:
- The linear speed of rotation of the earth is the maximum at the equator and reduces towards the poles.
- Therefore rockets are launched closer to the equator so that it provides an initial truth during the launching.
Revolution of the earth (7:43 PM)
- Revolution is the movement of the earth around the sun.
- Earth revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit.
- The period of the revolution of the earth is 365 days and 6 hrs.
- The average speed of the revolution of the earth is nearly 1 lakh Km/hr.
- The direction of the revolution is in the anti-clockwise direction.
- Perihelion is the position of the earth nearest to the sun (On 3rd January).
- Aphelion is the position of the earth farthest from the sun (On July 4th).
Seasons (7:56 PM)
- Geographical there are 4 seasons- Summer, Winter, Autumn, and Spring.
The topic for the next class: The occurrence of Seasons on earth.